Atomic Number 12
In the modern periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons define the identity of an element (i.e., an element with 6 protons is a carbon atom, no matter how many neutrons may be present). The number of protons determines how many electrons surround the nucleus, and it is the arrangement of these electrons that determines most of the chemical behavior of an element.
You are in the right place and time to meet your ambition. In fact, this topic is meant to untwist the answers of CodyCross Atomic number 12, abundant element from stars. Accordingly, we provide you with all hints and cheats and needed answers to accomplish the required crossword and find a final word of the puzzle group. Magnesium has an atomic number of 12. Which of the following statements is true of a neutral magnesium atom? It has 12 protons, 12 electrons, and 12 neutro.

In a periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements having similar chemical properties naturally line up in the same column (group). For instance, all of the elements in Group 1A are relatively soft metals, react violently with water, and form 1+ charges; all of the elements in Group 8A are unreactive, monatomic gases at room temperature, etc. In other words, there is a periodic repetition of the properties of the chemical elements with increasing mass.
In the original periodic table published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869, the elements were arranged according to increasing atomic mass— at that time, the nucleus had not yet been discovered, and there was no understanding at all of the interior structure of the atom, so atomic mass was the only guide to use. Once the structure of the nucleus was understood, it became clear that it was the atomic number that governed the properties of the elements.
Learning Objective
- Determine the relationship between the mass number of an atom, its atomic number, its atomic mass, and its number of subatomic particles
A-(Atomic number 12) = Magnesium B-(Atomic number 18) = Argon C-(Atomic number 20) = Calcium Element Calcium and magnesium will show similar properties as they belong to the same group (Group II) of the periodic table. They have the same number of valence electrons and they both are metals. While argon is a noble gas. The atomic number of an element is equal to the total number of protons in the nucleus of the atoms of that element. The atomic number can provide insight into the electronic configuration of the element. For example, carbon has an electron configuration of He 2s 2 2p 2, since its atomic number is 6.
Key Points
- Neutral atoms of each element contain an equal number of protons and electrons.
- The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number and is used to distinguish one element from another.
- The number of neutrons is variable, resulting in isotopes, which are different forms of the same atom that vary only in the number of neutrons they possess.
- Together, the number of protons and the number of neutrons determine an element’s mass number.
- Since an element’s isotopes have slightly different mass numbers, the atomic mass is calculated by obtaining the mean of the mass numbers for its isotopes.
Terms
- atomic massThe average mass of an atom, taking into account all its naturally occurring isotopes.
- mass numberThe sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom.
- atomic numberThe number of protons in an atom.
Atomic Number
Neutral atoms of an element contain an equal number of protons and electrons. The number of protons determines an element’s atomic number (Z) and distinguishes one element from another. For example, carbon’s atomic number (Z) is 6 because it has 6 protons. The number of neutrons can vary to produce isotopes, which are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. The number of electrons can also be different in atoms of the same element, thus producing ions (charged atoms). For instance, iron, Fe, can exist in its neutral state, or in the +2 and +3 ionic states.
Mass Number
An element’s mass number (A) is the sum of the number of protons and the number of neutrons. The small contribution of mass from electrons is disregarded in calculating the mass number. This approximation of mass can be used to easily calculate how many neutrons an element has by simply subtracting the number of protons from the mass number. Protons and neutrons both weigh about one atomic mass unit or amu. Isotopes of the same element will have the same atomic number but different mass numbers.
Scientists determine the atomic mass by calculating the mean of the mass numbers for its naturally-occurring isotopes. Often, the resulting number contains a decimal. For example, the atomic mass of chlorine (Cl) is 35.45 amu because chlorine is composed of several isotopes, some (the majority) with an atomic mass of 35 amu (17 protons and 18 neutrons) and some with an atomic mass of 37 amu (17 protons and 20 neutrons).

Given an atomic number (Z) and mass number (A), you can find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a neutral atom. For example, a lithium atom (Z=3, A=7 amu) contains three protons (found from Z), three electrons (as the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons in an atom), and four neutrons (7 – 3 = 4).
Show Sources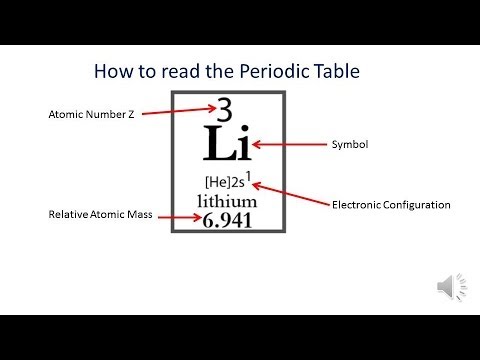
Atomic Number 12 Abundant Element From Stars
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources:
http://www.boundless.com/
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/atomic_number
Wiktionary
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/atomic-mass–2
Boundless Learning
CC BY-SA 3.0.
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/A-level_Chemistry/OCR/Atoms,_Bonds_and_Groups/Atoms_and_Reactions/Atoms
Wikibooks
CC BY-SA 3.0.
Atomic Number 120
http://cnx.org/content/m44390/latest/?collection=col11448/latest
OpenStax CNX
CC BY 3.0.
